what are virtual private network
In today’s digital age, the need for online security and privacy has become more crucial than ever before. As we navigate through a vast network of interconnected devices and platforms, our personal data is constantly at risk of falling into the wrong hands. This is where Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) come into play. A VPN provides a secure and private connection between your device and the internet, encrypting your data and routing it through a remote server. But what exactly is a VPN, how does it work, and why should you consider using one? In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of virtual private networks, shedding light on their importance in safeguarding our online presence from prying eyes while maintaining anonymity in an increasingly connected world.
What is a virtual private network?
A virtual private network (VPN) is a technology that allows users to create a secure and private connection over a public network, typically the internet. It enables individuals or organizations to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their devices were directly connected to a private network. By encrypting the data transmitted between the user’s device and the VPN server, VPNs provide an extra layer of security against potential threats such as hackers or surveillance.
VPNs are commonly used for various reasons, including enhancing online privacy, bypassing geo-restrictions, and securing remote connections. When using a VPN, all internet traffic is routed through the VPN server before reaching its destination. This process hides the user’s actual IP address and replaces it with one from the VPN server’s location. As a result, it becomes difficult for anyone monitoring internet activity to trace back actions to an individual user. In addition to privacy benefits, VPNs can also be beneficial for accessing content that may be blocked in certain regions due to geographical restrictions or censorship. By connecting to a server located in another country where the content is available, users can circumvent these barriers and access restricted websites or streaming platforms. Moreover, businesses often utilize VPNs for employees working remotely who need secure access to company resources while outside of their physical office space.
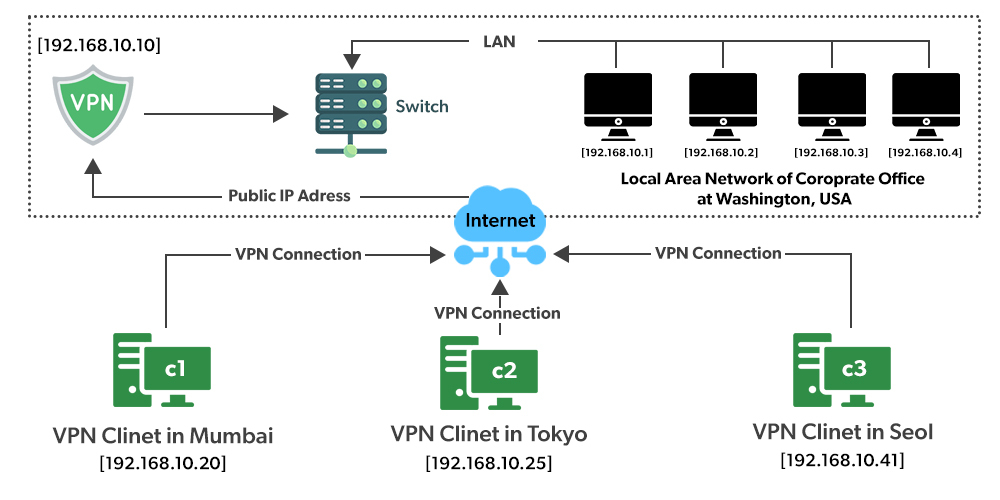
How does a VPN work?
A virtual private network (VPN) is a technology that allows users to create a secure connection over a public network, such as the internet. It encrypts the data transmitted between the user’s device and the VPN server, ensuring that it remains private and cannot be accessed by unauthorized individuals. When a user connects to a VPN, their device sends data through an encrypted tunnel to the VPN server. The server then decrypts this information and sends it to its intended destination, whether it’s a website, application, or another network. This process also works in reverse, with data from the destination being sent back through the VPN server and encrypted before reaching the user’s device.
VPNs provide several benefits, including enhanced security and privacy. By encrypting data traffic, they prevent hackers or other malicious actors from intercepting sensitive information like passwords or credit card details. Additionally, VPNs allow users to bypass censorship or geographical restrictions by masking their real IP address with one from another location.
Benefits of using a VPN
A virtual private network (VPN) is a technology that creates a secure connection over the internet, allowing users to access and transmit data privately and anonymously. One of the primary benefits of using a VPN is enhanced online privacy. By encrypting all internet traffic, VPNs prevent hackers, ISPs, or any other third parties from intercepting and accessing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, or browsing history.
In addition to privacy protection, another advantage of using a VPN is bypassing geo-restrictions. With a VPN, users can route their internet connection through servers located in different countries around the world. This allows them to appear as if they are accessing the internet from those locations. As a result, individuals can overcome regional content restrictions imposed by streaming services or websites and enjoy unrestricted access to their desired content. Moreover, using a VPN offers an added layer of security when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks. Public Wi-Fi hotspots are notorious for being vulnerable to cyber attacks since they often lack proper encryption measures. By connecting through a VPN while on public Wi-Fi, users can ensure that their data remains encrypted and protected from potential eavesdroppers or malicious actors lurking on these networks. Overall, employing a VPN provides numerous benefits including heightened privacy protection, bypassing geo-blocks for content access, and securing connections on public Wi-Fi networks.
Common uses for VPNs
A virtual private network (VPN) is a technology that allows users to create a secure connection over a public network such as the internet. It provides an encrypted and private tunnel for data transmission, ensuring confidentiality, anonymity, and security for users’ online activities. VPNs are commonly used for various purposes. One common use of VPNs is to enhance online privacy and security. By encrypting internet traffic, VPNs prevent hackers or eavesdroppers from intercepting sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, or personal data. This is especially important when using public Wi-Fi networks in cafes, airports, or hotels where the risk of cyber attacks is higher.
Another popular application of VPNs is bypassing geo-restrictions and accessing region-locked content. With a VPN connection, users can connect to servers located in different countries and appear as if they are browsing from those regions. This allows them to access websites or streaming platforms that may be blocked or restricted in their own country due to censorship laws or licensing agreements. Furthermore, businesses often use VPNs to provide remote access to employees working from home or traveling abroad. Through a VPN connection, remote workers can securely access company resources such as shared drives, internal applications, or email servers without compromising sensitive data.
Choosing the right VPN provider
A virtual private network (VPN) is a technology that allows users to create a secure connection over the internet. It encrypts the user’s data and routes it through a remote server, making it appear as if they are accessing the internet from that server’s location. VPNs provide enhanced privacy and security by masking the user’s IP address and protecting their online activities from potential threats such as hackers, government surveillance, or ISP monitoring.
Choosing the right VPN provider is crucial in ensuring an effective and reliable service. One important factor to consider is the provider’s logging policy. Opting for a VPN that follows a strict no-logs policy ensures that your online activities are not recorded or stored by the provider, enhancing your privacy. Additionally, evaluating the number of servers and their locations can help determine whether you will have access to desired content while maintaining good connection speeds. Another critical aspect when selecting a VPN provider is assessing its security features. Look for providers that offer strong encryption protocols such as OpenVPN or IKEv2, along with advanced features like a kill switch or DNS leak protection. These features provide added layers of security in case of unexpected disruptions in your VPN connection or potential vulnerabilities.
Potential drawbacks of using a VPN
A virtual private network (VPN) is a technology that allows users to establish a secure and encrypted connection over the internet. While VPNs offer numerous benefits, they also come with potential drawbacks. Firstly, using a VPN can slow down internet speed. This is because the encryption process adds an extra layer of security and can cause some delay in data transmission. Therefore, if you rely on high-speed internet for activities such as online gaming or streaming, using a VPN may not be ideal. Secondly, there are concerns about the privacy and trustworthiness of certain VPN providers. Not all VPN services are created equal, and some may log user activity or sell their data to third parties without their consent. It is important to thoroughly research and choose a reputable VPN provider that respects your privacy rights.
Lastly, some websites and online services block or restrict access to users who connect through a VPN. These platforms do this to prevent unauthorized access or misuse from certain locations or IP addresses associated with VPN servers. Therefore, you may encounter difficulties accessing specific content while using a VPN. Although virtual private networks bring valuable security benefits for protecting online privacy and maintaining anonymity, there are potential drawbacks such as reduced internet speed, privacy concerns regarding certain providers’ practices, and restricted access to certain websites or services.
Conclusion: Importance and future of VPNs.
In conclusion, virtual private networks (VPNs) are powerful tools that provide users with a secure and private internet connection. By encrypting their data and masking their IP addresses, VPNs ensure that users can browse the web anonymously and protect their sensitive information from hackers and surveillance. Additionally, VPNs allow users to bypass geo-restrictions and access content that may be blocked in their region. With the increasing threat of cybercrime and online censorship, it is essential for individuals and businesses to consider using a VPN to safeguard their online activities. So, whether you want to protect your personal privacy or enhance your online security, investing in a reliable VPN is definitely worth considering.
ALSO READ / best seo agencies in miami





